[ad_1]
Apple Fellow Phil Schiller, the executive in charge of leading the App Store, testified in court on Monday that he had originally raised concerns about the 27% commission the iPhone maker planned to charge app developers on any purchases made outside the App Store. In addition to being a potential compliance risk, he suggested that the fee would create an “antagonistic relationship” between Apple and developers and seemed to require Apple to have audit rights to check whether or not they owed Apple money for the transactions that took place outside the App Store.
Build a website that pays you back with real revenue.
Apple typically charges a 30% commission on in-app purchases, but the reduced fee of 27% was a result of the Epic Games-Apple ruling. In 2021, the court determined that although the tech giant was not a monopolist, it would have to stop blocking app developers from linking to other ways for customers to pay beyond Apple’s own in-app purchases (IAP).
Apple technically complied with the ruling by changing its App Store Guidelines to permit developers to link to their websites from their iOS and iPadOS apps to give customers an alternative way to pay.
However, Apple only reduced its commission by 3% for these purchases.
At the time, Fortnite maker Epic Games CEO Tim Sweeney called out Apple for “bad-faith” compliance, saying the tech company undermined the 2021 order from U.S. District Judge Yvonne Gonzalez Rogers, which had granted developers the right to add buttons or links to other purchasing mechanisms in addition to Apple’s IAP.
Apple and Epic Games have since returned to federal court so Rogers could determine whether Apple violated her original order that forced the App Store to open to more competition.
According to Schiller’s testimony, he initially objected to commissions on these outside purchases.
“… I had great concerns about the collections of funds from developers,” he said, specifically “the change in the role of the App Store to now an organization that needs to collect money from developers.”
He said he was worried about how the App Store would have to go after developers who didn’t pay the commissions, making it “some kind of a collection agency” that had “rules around how we handle nonpayment and whether ultimately it means we’re going to have to do audits of developers.”
Schiller said he worried about “how all of those things change the relationship between Apple and developers in a way I thought would be detrimental.”
The hearing has unearthed the extensive process Apple underwent while debating the merits of still charging a fee. With hosts of documents and emails, lawyers detailed the back-and-forth that took place internally at Apple as executives weighed different options regarding its compliance with the court’s order.
Despite the initial concerns Schiller raised, a pricing committee that included Apple CEO Tim Cook, former CFO Luca Maestri, and Apple’s legal team, alongside Schiller, ultimately decided to charge developers a commission on these outside purchases.
The company also decided the same 3% fee reduction would apply to developers in its Small Business Program, lowering their already reduced commission of 15% to 12% for transactions outside the App Store.
Documents referenced in court indicated that Apple analyzed the financial impact on developers who chose to link out to their own websites.
In one model, for example, Apple worked to determine how the “less seamless experience” of using a non-IAP method would lead customers to abandon their transactions. By modeling where this tipping point was, Apple was able to determine when the links would stop being an advantage to developers, which would push them back to using IAP.
Apple also found that more restrictive rules around the placement and formatting of the links themselves could reduce the number of apps that decided to implement these outside links. The company looked into the financial impact of excluding some other partners — like those in its video and news programs — from the new program.
The company weighed different options for when to charge commissions, too. At one time, it thought to charge its 27% fee on external purchases that took place within 72 hours of when the link was clicked. When the new guidelines went live, however, that time frame had been stretched to seven days.
Lawyers suggested Cook himself was involved with how the warning to App Store customers would appear, recommending an update to the text that appears when the external links were clicked. In one version, that link warned customers they were “no longer transacting with Apple.” Later, the link was updated to subtly suggest there could be privacy or security risks with purchases made on the web.
In another meeting about the commissions, people had also expressed concerns about Apple charging for web transactions.
“This might be perceived like we’re trying to charge for what happens on the internet,” one of the notes from the meeting said.
[ad_2]
Source link
Related posts:
Stay Safe Online: Essential Tips for Safer Internet Day
Is Your Phone Your Best Friend or a Silent Spy?
Wipe Your Digital Footprints with Data Wipe Software
No, you’re not fired – but beware of job termination scams
DeceptiveDevelopment targets freelance developers
Fake job offers target coders with infostealers
Belarus-Linked Ghostwriter Uses Macropack-Obfuscated Excel Macros to Deploy Malware
LightSpy Expands to 100+ Commands, Increasing Control Over Windows, macOS, Linux, and Mobile
CISA Adds Microsoft and Zimbra Flaws to KEV Catalog Amid Active Exploitation
Malicious PyPI Package "automslc" Enables 104K+ Unauthorized Deezer Music Downloads
CERT-UA Warns of UAC-0173 Attacks Deploying DCRat to Compromise Ukrainian Notaries
Three Password Cracking Techniques and How to Defend Against Them
New Linux Malware ‘Auto-Color’ Grants Hackers Full Remote Access to Compromised Systems
SOC 3.0 - The Evolution of the SOC and How AI is Empowering Human Talent
Leaked Black Basta Chat Logs Reveal $107M Ransom Earnings and Internal Power Struggles
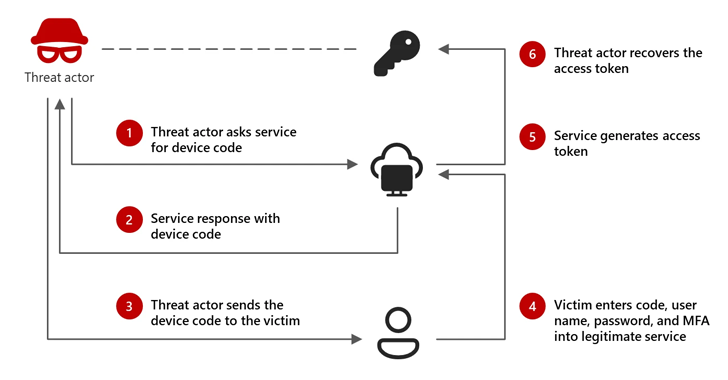
Microsoft: Russian-Linked Hackers Using 'Device Code Phishing' to Hijack Accounts
AI-Powered Social Engineering: Ancillary Tools and Techniques
Lazarus Group Deploys Marstech1 JavaScript Implant in Targeted Developer Attacks
New “whoAMI” Attack Exploits AWS AMI Name Confusion for Remote Code Execution
Android's New Feature Blocks Fraudsters from Sideloading Apps During Calls
New Golang-Based Backdoor Uses Telegram Bot API for Evasive C2 Operations
⚡ THN Weekly Recap: Google Secrets Stolen, Windows Hack, New Crypto Scams and More
CISO's Expert Guide To CTEM And Why It Matters
South Korea Suspends DeepSeek AI Downloads Over Privacy Violations
Microsoft Uncovers New XCSSET macOS Malware Variant with Advanced Obfuscation Tactics
Cybercriminals Exploit Onerror Event in Image Tags to Deploy Payment Skimmers
New Xerox Printer Flaws Could Let Attackers Capture Windows Active Directory Credentials
Winnti APT41 Targets Japanese Firms in RevivalStone Cyber Espionage Campaign
Juniper Session Smart Routers Vulnerability Could Let Attackers Bypass Authentication
Debunking the AI Hype: Inside Real Hacker Tactics
Build a website that pays you back with real revenue.